Growing vegetables in your greenhouse is a great way to have fresh produce all year round. It is also a calming and a fantastic way to pass the time. Do not let this task intimidate you because we are here to help.
In this guide, we will walk you through the basics of greenhouse gardening for beginners!
Step-by-Step Guide on Greenhouse Gardening for Beginners
STEP # 1: Choosing the Site for Your Greenhouse
Choose the Nearest Location
Consider following a basic rule of thumb: choose thenearest site to your house or garden. This will encourage you to use your garden regularly and will allow you to show off your greenhouse to your guests.
Access to Water and Electricity
Also, consider appropriate access to water and electricity. Remember that the main advantage of a greenhouse is how you can extend your growing season. To do this, you need to simulate certain environmental conditions, like heat and light.
If you plan to plant many vegetables, it will also be much easier to have immediate and regular water access and not have to lug buckets to and from your house.
Proper Leveling and Sunlight
You need a combination of a level area with the maximum exposure to the sun during the day.
If you can, find a place where the greenhouse will get at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day during the winter. However, if your area does not have this, consider getting grow lights to simulate sunlight.
If you live in hot areas, deciduous trees can provide much-needed shade in the summer while also allowing proper sunlight during the winter because they lose their leaves during fall.
Avoid areas near coniferous trees or other things that will cast a shadow during the long winter months.
Adequate Drainage
While a greenhouse can be placed almost anywhere, you must ensure there is adequate drainage.
Ideally, you should lay a cloth over the area you intend to use for your greenhouse. Then, cover the cloth with 3 inches of 1/4-inch gravel.
This not only keeps the weeds out but also ensures you will always have adequate drainage.
Infographic

STEP #2: Building the Frame of Your Greenhouse
The frame is the skeleton of your greenhouse. This is the first thing you build on the site you have selected.
The type of greenhouse you choose will depend on different factors. Below are some of the types you can consider.
Types of Greenhouses
Figuring out the right type of greenhouse to build on your property is the first crucial step. You need to consider how much growing space you will need because a greenhouse is a long-term investment. It has to be big enough for years to come.
You also want to maximize the light and headroom in your greenhouse, especially if you’re going to grow hanging plants.
Attached Greenhouse
Attached or lean-to greenhouses are great if you do not want to build all four walls for your greenhouse.
It also uses a sturdy, weight-bearing wall (your home or garage) so the other three sides can be made lighter.
They are often less expensive than other greenhouse models available and are excellent for growing herbs, seedlings, and some vegetables.
We highly recommend this if you have limited space for your greenhouse or cannot afford to start with a standalone structure.
The downside to this is that the amount of sunlight that can go into your greenhouse is limited by installing the three sides.
Freestanding Greenhouse
A freestanding greenhouse is a structure that can stand on its own. This gives you a lot of freedom to decide where you want to place the greenhouse on your property.
Some critical requirements for a standalone greenhouse are:
- The ground must be level.
- The area must receive plenty of sunlight.
While this type may be more expensive initially, they provide a lower cost per plant in the long run because you can grow a lot more in them.
In most areas, it also allows you to start the growing season much earlier and extend the season by bringing the plants at the first sign of frost.
The other advantage is it can be a sanctuary away from your house. You can get out and enter your oasis to focus on your plants.
You can also install a separate heating system if you live in a particularly cold area during winter.
STEP# 3: Putting Your Greenhouse Glazing Material
Now that you have your frame, it is time to fill up the walls.
Glazing refers to the covering around the frame of your greenhouse. It allows sunlight and warmth in, while keeping out the rest of the elements. The most traditional glazing material is glass. However, it is also the most expensive.
A more inexpensive alternative is plastic sheeting. This material’s disadvantage is that it degrades quickly, especially if you frequently experience strong winds or rain in your area.
A good middle groundis polycarbonate material. It is more affordable than glass, lightweight, and retains heat better than either glass or plastic.
Moreover, it can be used on flat or bent surfaces, is very durable, and transmits light very well.
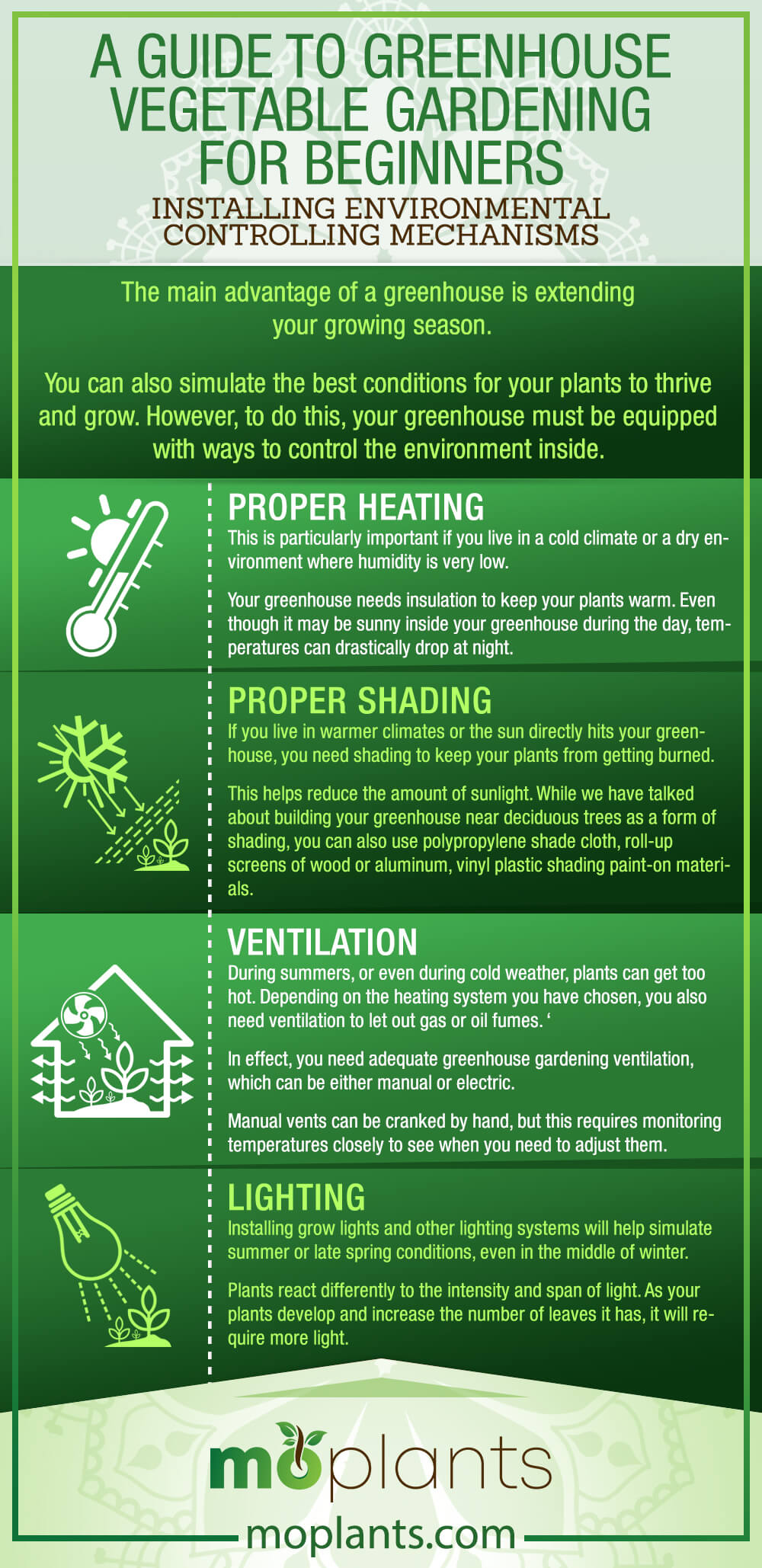
STEP #4: Installing Environmental Controlling Mechanisms
As we have said, the main advantage of a greenhouse is extending your growing season.
You can also simulate the best conditions for your plants to thrive and grow. However, to do this, your greenhouse must be equipped with ways to control the environment inside.
#1: Proper Heating
This is particularly important if you live in a cold climate or a dry environment where humidity is very low.
Your greenhouse needs insulation to keep your plants warm. Even though it may be sunny inside your greenhouse during the day, temperatures can drastically drop at night.
Calculate How Much Heat Loss There is
To heat your greenhouse efficiently, you must match the equipment you will install to the types of crops you produce. Calculate the greenhouse’s heat loss, then choose a system with the right type and capacity to suit this need.
Install Thermostats and Controls
There are various types of thermostats and environmental controllers that you can find for commercial greenhouses. They range from very simple to sophisticated systems. Regardless, there are some fundamental factors that you need to consider.
Place Sensing Devices At Plant Level
Your sensing device measures the temperature around the sensors.
Since you are trying to maintain the ideal temperature for your plants, it only makes sense that the sensing device must be at the plant level.
While thermostats at eye level are easier to read, they do not provide the accurate and necessary data for optimum environmental control.
Ensure the Appropriate Number of Sensors
Depending on how big your greenhouse is, you may need more than one thermostat or sensor.
Temperatures and environmental conditions can often vary significantly, even within small distances. So it is crucial to make sure you have the correct number to ensure proper greenhouse gardening conditions.
Do Not Place Them Under the Sun
This is quite obvious, but it needs to be said anyway. Placing your thermostat under direct sunlight will result in inaccurate temperature readings.
Mount your sensors so that they face north or in a protected location. Sometimes, it is also better to use a small fan to pull air over the sensor to get accurate readings.
PRO TIP
You can place rocks or barrels of water inside your greenhouse to capture heat from the sun and help keep your plants warm during cooler evenings.
However, rely on this as these items will also lose heat throughout the night at uncontrollable rates.
Consider evaporative cooling systems, too. This helps regulate temperatures and add moisture back inside the greenhouse to help humidity levels, which is essential if you live in a dry climate.
#2: Proper Shading
If you live in warmer climates or the sun directly hits your greenhouse, you need shading to keep your plants from getting burned.
This helps reduce the amount of sunlight. While we have talked about building your greenhouse near deciduous trees as a form of shading, you can also use polypropylene shade cloth, roll-up screens of wood or aluminum, vinyl plastic shading paint-on materials.
Depending on your location, you may need permanent shading solutions, like paint-on materials, or adjustable ones, like roll-up screens.
The former is hot all year round, and the latter is when you have drastic changes in temperature from really hot to cold throughout the year.
#3: Ventilation
During summers, or even during cold weather, plants can get too hot. Depending on the heating system you have chosen, you also need ventilation to let out gas or oil fumes. ‘
In effect, you need adequate greenhouse gardening ventilation, which can be either manual or electric.
Manual vents can be cranked by hand, but this requires monitoring temperatures closely to see when you need to adjust them.
There are also electric and temperature-sensitive hydraulic vents that automatically close and open on their own when certain temperature conditions are met.
It is also good to install an oscillating fan inside your greenhouse to keep the air moving. This will also help prevent many diseases from spreading among your plants.
#4: Lighting
As we have briefly mentioned earlier, installing grow lights and other lighting systems will help simulate summer or late spring conditions, even in the middle of winter.
The factors you should consider when choosing the proper lighting for you are:
- The type and variety of plants you are growing
- The season
- How much daylight you have
- How much sunlight you need
Plants react differently to the intensity and span of light. As your plants develop and increase the number of leaves it has, it will require more light.
Note that numerous human-made light sources with many color blends may not be enough for your plants’ photosynthetic requirements.
LED grow lights and fluorescent lamp strips are high output lighting systems crucial to photosynthesis and proper plant germination.
They are also incredibly useful because they can cover a larger surface area and output.
Fluorescent lighting is typically used in greenhouse growing if you want a weak natural light.
Infographic
STEP #5: Accessorize Your Greenhouse
Now that you have the essential elements for your green house gardening, you can install various accessories. For example, you may need shelving or storage areas for your equipment and tools. You can also install a tool rack, a potting bench, and more.
If humidity is a constant problem in your area, adding a mist system will introduce more humidity inside your greenhouse. If you intend to also relax in your greenhouse, perhaps some seating will be good.
Depending on your budget, you can make your greenhouse as beautiful or as functional as you want.
Make sure to consider what your plants need and the amount of space you have. Just remember that it is better to spend more on a suitable environmental control system than on decorations.
STEP #6: Planting in Your Greenhouse
What Should I Plant in My Greenhouse?
The great news is that one can plant anything and everything in your new greenhouse.
However, if you want to grow vegetables that are best suited for your set-up, here are a few plants you may want to grow in a greenhouse.
- Peas
- Radishes
- Garlic
- Leafy Greens
- Strawberries
- Onions
- Tomatoes
- Sunflowers
- Mushrooms
- Potatoes
All you need to remember is that the conditions in your greenhouse and the controls you have for the environment must suit the type of plants and vegetables you are gardening.
For beginners, start with one or two vegetables.
STEP #7: Watering Your Plants
Improper watering is the most significant contributor to the failure of greenhouse gardening. Most water their plants and vegetables according to a set schedule.
When watering your vegetables, beginners have to remember several variables you need to consider.
The temperature, growth stage, and humidity will affect your plants. Beginners should use a moisture meter to know when you need to water.
STEP #8: Protecting Your Plants from Pests
Pests are very dangerous in greenhouses because of the enclosed environment and cost of growing even just one plant.
Install insect screens on the air intakes and check all plants for insects and pests before bringing them inside the garden.
Clean all your tools regularly and bring good bugs that eat the harmful insects inside. You can also spray insect repellants and sprays.
Infographic

Conclusion
Greenhouse gardening is one hobby that is certainly worth it. With all these tips for beginners, you are well-equipped to start your very own project.


